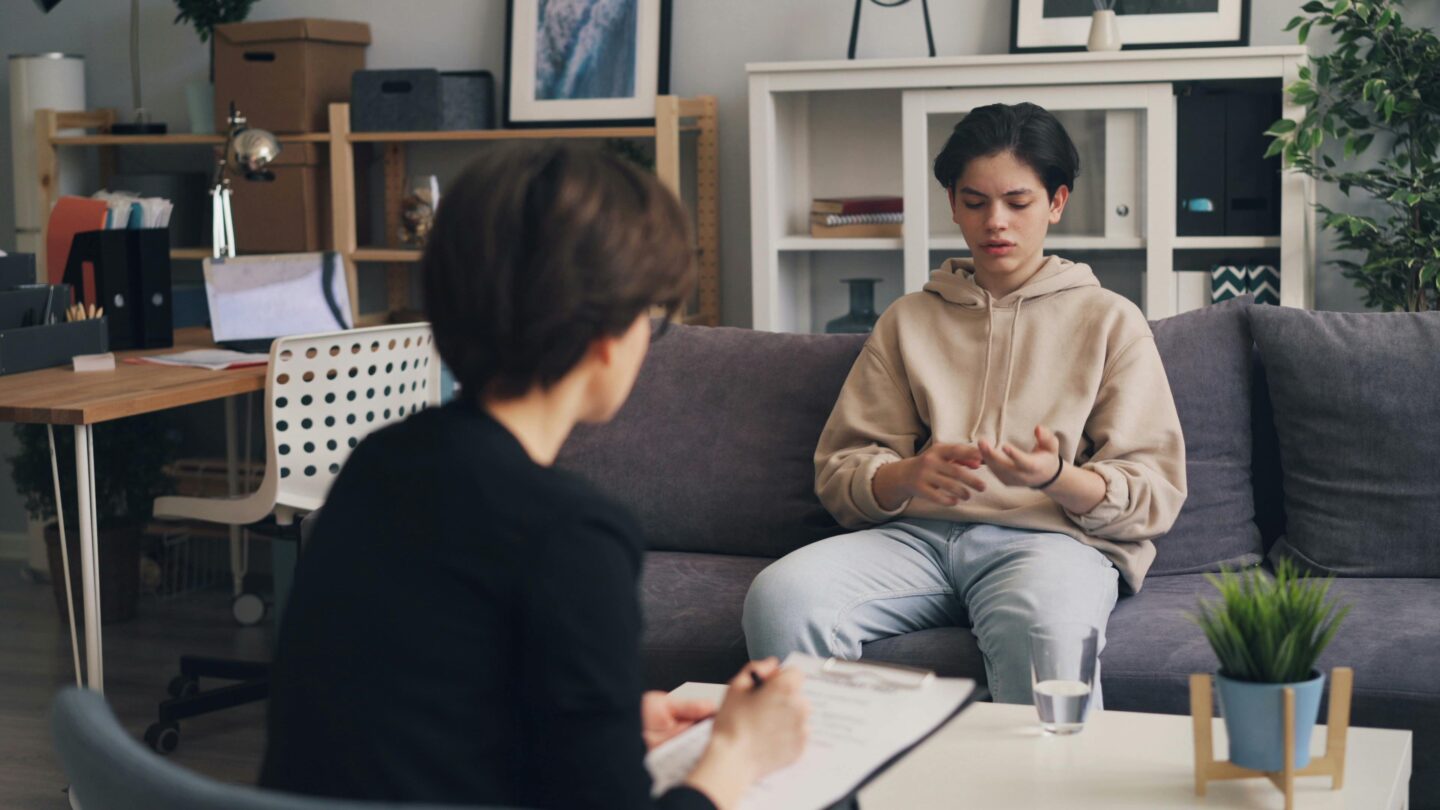
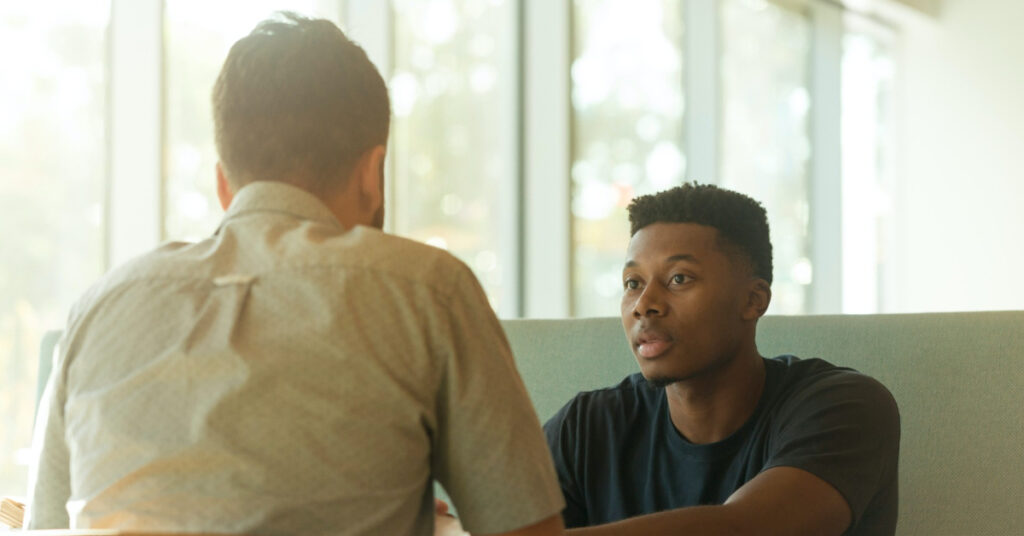
Talk therapy, also known as psychotherapy or counseling, is a therapeutic approach that helps individuals explore and address emotional and psychological issues through verbal communication with a trained therapist. It is widely used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, relationship problems, and trauma.
In this post, we’ll explore the different types of talk therapy, how they work, and how they can help individuals manage their mental health more effectively. Whether you’re considering therapy for the first time or looking to understand its different forms, this guide will provide insight into the traditional, talk-based approaches to healing.
The Role of Talk Therapy in Mental Health Treatment
Talk therapy plays an essential role in mental health treatment by providing a safe and supportive space for individuals make progress. It allow individuals to express their feelings, gain self-awareness, and learn healthier ways to cope with emotional distress. It is an effective way to address a range of issues, from stress and anxiety to trauma and relationship struggles.
Here are a few key reasons why talk therapy is important for mental well-being:
1. Facilitates Emotional Expression
Talking about emotions can often be difficult, especially when dealing with complex feelings of sadness, anger, or fear. Therapy provides a non-judgmental space to explore these emotions and gain clarity.
Example: A person may struggle with the loss of a loved one, and talk therapy allows them to express their grief, helping them process their emotions in a healthy way.
2. Provides Insight and Self-Awareness
Talk therapy helps individuals gain insights into their behaviors, thought patterns, and emotions. By understanding these factors, people can identify areas in their life that need attention and work toward meaningful change.
Example: Through therapy, an individual may discover that their anxiety is rooted in negative thought patterns or past experiences that need to be addressed.
3. Helps Build Coping Skills
In therapy, individuals learn practical tools and strategies for coping with stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges. These coping mechanisms can improve emotional regulation and overall well-being.
Example: A person struggling with anxiety may learn relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, or cognitive strategies to challenge negative thoughts.
Different Types of Talk Therapy and How They Work
There are various types of talk therapy, each with its own approach and focus. Below are some of the most well-known traditional talk-based therapies and how they work:
Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic therapy is rooted in the belief that unconscious thoughts and past experiences influence current behavior and emotions. In addition, it focuses on exploring early childhood experiences, unresolved conflicts, and the unconscious mind to gain insight into the root causes of emotional distress.
- How it works: In psychodynamic therapy, the therapist helps the client explore past experiences and unconscious patterns that may be affecting their present behavior. The goal is to bring these unconscious issues into the client’s awareness so they can address them and make healthier choices moving forward.
- Example: If a client is struggling with relationship issues, psychodynamic therapy may explore their early attachment to parents or caregivers to understand how these relationships influence their current relationship patterns.
Person-Centered Therapy
Person-centered therapy, developed by Carl Rogers, emphasizes the importance of a supportive, empathetic relationship between therapist and client. The therapist provides unconditional positive regard, which helps clients feel accepted and understood, fostering personal growth and self-discovery.
- How it works: In this approach, the therapist listens actively without judgment, allowing the client to explore their feelings and experiences at their own pace. In additional, the therapist’s role is to create a safe, non-directive space where the client feels free to express themselves openly.
Example: A client struggling with low self-esteem may benefit from person-centered therapy, as the therapist provides acceptance and empathy, helping the client feel more confident and validated in their feelings.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a structured, goal-oriented therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns that contribute to emotional distress. It’s widely used for treating anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders.
- How it works: CBT focuses on the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. The therapist helps the client identify distorted or unhelpful thinking patterns and replace them with more realistic and positive thoughts. CBT also includes behavioral techniques that help clients change unhealthy behaviors.
Example: A teen with social anxiety may use CBT to challenge irrational thoughts about social situations. CBT will also allow the teen to practice exposure exercises to build confidence in social settings.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
DBT is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy that was developed to help individuals with intense emotional regulation issues, often seen in conditions like borderline personality disorder. It focuses on balancing acceptance with change, and emphasizes mindfulness, distress tolerance, and emotional regulation.
- How it works: DBT combines individual therapy with skills training in various areas. These include mindfulness, emotion regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, and distress tolerance. The goal is to help individuals manage overwhelming emotions and build healthier coping strategies.
Example: A person dealing with intense emotional outbursts may learn DBT skills to manage their emotions. This allows them to engage in healthier ways of communicating with others.
Humanistic Therapy
Humanistic therapy, similar to person-centered therapy, focuses on the individual’s capacity for self-actualization and personal growth. Additionally, it emphasizes free will, self-discovery, and the belief that people can change and grow to achieve their fullest potential.
- How it works: The therapist provides a compassionate and accepting environment, where the client is encouraged to explore their own feelings, goals, and values. The therapy is non-directive, meaning that the therapist follows the client’s lead in the conversation.
Example: A person who is feeling stuck in life may benefit from humanistic therapy. By gaining insight into their true desires and values, which helps them make more authentic decisions.

How to Choose the Right Type of Talk Therapy
Choosing the right type of talk therapy depends on the individual’s needs, preferences, and the nature of the issues. Here are a few things to consider:
- For unresolved childhood issues: Psychodynamic therapy might be a good option.
- For emotional regulation and mindfulness: Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) can be very effective.
- For challenging negative thoughts: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a popular and proven approach.
- For personal growth and self-awareness: Person-centered therapy or humanistic therapy may be helpful.
You can work with a mental health professional to help you decide which approach is best for you.
The Power of Talk Therapy in Mental Health
Talk therapy provides a safe and supportive space to explore emotions, gain insights, and learn coping skills. By engaging in different types of talk therapy, individuals can find the tools they need to lead healthier lives.
If you or someone you know is considering therapy, know that help is available. Additionally, therapy can empower you to work through difficult emotions, build resilience, and create meaningful change in your life.
Contact us today. Schedule an appointment with one of our compassionate therapists. We’re here to help you navigate through your challenges and support your mental well-being.